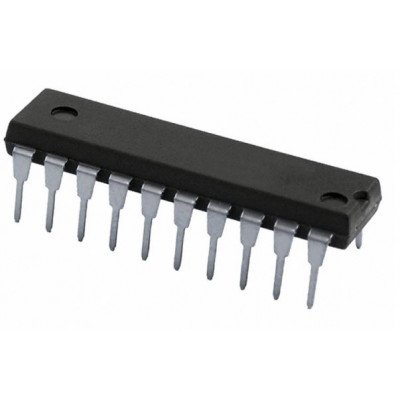
74LS669 Synchronous 4-Bit Up/Down Binary Counter IC (74669) DIP-14 Package
The 74LS669 is a synchronous 4-bit up/down counter. The LS669 is a 4-bit binary counter. For high speed counting applications, this presettable counter features an internal carry lookahead for cascading purposes. By clocking all flip-flops simultaneously so the outputs change coincident with each other (when instructed to do so by the count enable inputs and internal gating) synchronous operation is provided. This helps to eliminate output counting spikes, normally associated with asynchronous (ripple-clock) counters. The four master-slave flip-flops are triggered on the rising (positive-going) edge of the clock waveform by a buffered clock input. Circuitry of the load inputs allows loading with the carry-enable output of the cascaded counters. Because loading is synchronous, disabling of the counter
Apple Shopping Event
Hurry and get discounts on all Apple devices up to 20%
Sale_coupon_15
₹53.10
Inclusive of GST
- Pick up from the Robotwala Store
To pick up today
Free
- Shiprocket from Air
Our courier will deliver to the specified address
3-4 Days
139
- Shiprocket from Surface
courier will deliver to the specified address
5-7 Days
90
- Warranty 1 year
- Free 30-Day returns
Payment Methods:
Description
The 74LS669 is a synchronous 4-bit up/down counter. The LS669 is a 4-bit binary counter. For high speed counting applications, this presettable counter features an internal carry lookahead for cascading purposes. By clocking all flip-flops simultaneously so the outputs change coincident with each other (when instructed to do so by the count enable inputs and internal gating) synchronous operation is provided. This helps to eliminate output counting spikes, normally associated with asynchronous (ripple-clock) counters. The four master-slave flip-flops are triggered on the rising (positive-going) edge of the clock waveform by a buffered clock input. Circuitry of the load inputs allows loading with the carry-enable output of the cascaded counters. Because loading is synchronous, disabling of the counter
by setting up a low level on the load input will cause the outputs to agree with the data inputs after the next clock pulse. Cascading counters for N-bit synchronous applications are provided by the carry look-ahead circuitry, without additional gating. Two count-enable inputs and a carry output help accomplish this function. Count-enable inputs (P and T) must both be low to count. The level of the up-down input determines the direction of the count. When the input level is low, the counter counts down, and when the input is high, the count is up. Input T is fed forward to enable the carry output. The carry output will now produce a low level output pulse with a duration ? equal to the high portion of the QA output when counting up and when counting down ? equal to the low portion of the QA output. This low level
carry pulse may be utilized to enable successive cascaded stages. Regardless of the level of the clock input, transitions at the P or T inputs are allowed. By diode-clamping all inputs, transmission line effects are minimized which allows simplification of system design. Any changes at control inputs (ENABLE P, ENABLE T, LOAD, UP/DOWN) will have no effect on the operating mode until clocking occurs because of the fully independent clock circuits. Whether enabled, disabled, loading or counting, the function of the counter is dictated entirely by the conditions meeting the stable setup and hold times.
Features :-
- Programmable Look-Ahead Up/Down Binary/Decade Counters
- Fully Synchronous Operation for Counting and Programming
- Internal Look-Ahead for Fast Counting
- Carry Output for n-Bit Cascading
- Fully Independent Clock Circuit
- Buffered Outputs
Specifications :-
- Supply Voltage : 4.75 – 5.25V
- Operating Ambient Temperature Range : 70?C
- Output Current ? High : ?0.4mA
- Output Current ? Low : 8.0mA
- Input HIGH Voltage : 2.0V
- Input LOW Voltage : 0.8V
- Input Clamp Diode Voltage : -0.65 – -1.5V
- Short Circuit Current : -100mA
- Power Supply Current : 34mA
Package Includes :-
1 X 74LS669 Synchronous 4-Bit Up/Down Binary Counter IC (74669) DIP-14 Package
Additional information
Operating voltage | 2.5 3.0V |
Pixel Resolution | 0.3MP |
Photosensitive array | 640 x 480 |
Optical Size | 1.6 inch |
Angel of view | 67 degrees |
Maximum Frame Rate | 30fps VGA |
Sensitivity | 1.3V/(Lux-sec) |
Dormancy | Less than 20A |
Power consumption | 60mW/15fpsVGA YUV |
Temperature operation Range | -30 C ~ 70 C |
Pixel area | 3.6 x 3.6 m |
Signal to noise ratio (SNR) | 46 dB |
Dynamic range | 52 dB |












 Boards & Modules
Boards & Modules ARM Microcontroller
ARM Microcontroller AVR Microcontroller Board
AVR Microcontroller Board Arduino boards
Arduino boards Advance Development Boards
Advance Development Boards 8051 Development Board
8051 Development Board
 Audio Amplifier Module
Audio Amplifier Module Current & Volatage Sensor
Current & Volatage Sensor Breakout Board
Breakout Board Flame Sensors
Flame Sensors Force Sensor
Force Sensor Gas Sensors
Gas Sensors Hall Effect Sensor
Hall Effect Sensor Humidity & Temperature Sensor
Humidity & Temperature Sensor LED Module
LED Module PIR Sensor
PIR Sensor Pressure Sensors
Pressure Sensors Proximity Sensor
Proximity Sensor Relay Module
Relay Module Real Time Clock (RTC) Module
Real Time Clock (RTC) Module Touch Sensor
Touch Sensor Ultrasonic Sensor
Ultrasonic Sensor Water Level & Water Flow Sensor
Water Level & Water Flow Sensor Weighing Scale Sensor
Weighing Scale Sensor




 Ai Thinker ESp Wifi Module
Ai Thinker ESp Wifi Module Pic Devlopment Board & programmer
Pic Devlopment Board & programmer Led lights & Strips
Led lights & Strips PCBs & Breadboard
PCBs & Breadboard Potentiometer
Potentiometer Power Transistors
Power Transistors Resistor & Smd & inductor
Resistor & Smd & inductor Switches
Switches Aluminium Heat Sink
Aluminium Heat Sink Buzzer & Speaker
Buzzer & Speaker capacitor
capacitor Crystal Oscillators
Crystal Oscillators Doides
Doides Electric Fuses
Electric Fuses ICs & Dips
ICs & Dips Power supply module
Power supply module Transformer
Transformer Relay Module
Relay Module Kits
Kits Magnet
Magnet RF Connectors
RF Connectors PCT and DC Connectors
PCT and DC Connectors Wires & Heat Shrink
Wires & Heat Shrink FFC, FPC, Berg connectors
FFC, FPC, Berg connectors
 Nextion
Nextion Segment
Segment Seedstudio
Seedstudio Waveshare
Waveshare E Bike Batteries
E Bike Batteries E bike Battery Case
E bike Battery Case E bike Connectors
E bike Connectors E bike Display
E bike Display E bike Kit
E bike Kit E bike Motors & Controllers
E bike Motors & Controllers Electronics Accessories
Electronics Accessories Mechanical Accessories
Mechanical Accessories
 Display
Display Cameras
Cameras
Reviews
There are no reviews yet.